Foods that contain vitamin D are essential for the proper functioning of the body. There are many foods that contain Vitamin D, especially in fish. There are also vitamin D supplements. Find out what are the main foods that contain vitamin D.Let us first talk about vitamin D.
Vitamin D is one of the vitamins that are very important to maintain the health of the body and maintains bone health from premature fragility, which is a type of vitamins that are difficult to obtain from food only. Today we will learn more about the benefits of vitamin D for the body and know what are the symptoms of its deficiency.
1. The main foods that contain vitamin D
In general, plant foods, such as fresh fruits and vegetables, provide very little vitamin D to the body. Only mushrooms contain an interesting amount of this vitamin. It is, therefore, necessary to choose other foods that contain vitamin D.
1.1 Mushrooms
Mushrooms are among the plant foods that contain vitamin D, since, some types of mushrooms are treated with ultraviolet light, which enhances the ability of the mushrooms to manufacture more vitamin D.Scientific research has shown that a UV-treated portobello contains a large amount of vitamin D, which helps in bone growth and strength in a great way.
1.2 Fish
Among the foods that contain vitamin D is fish, but not just any;
- Salmon: it is a good source of vitamin D. A portion of it, equivalent to 100 grams, contains 361-685 IU of this vitamin. It is worth noting that wild species of salmon contain more amounts of vitamin compared to the types found in fish farms.
- Sardine and herring: Where herring are a common fish, which is eaten raw, canned, or pickled, one serving of raw herring contains 1,628 international units of vitamin D, an amount equal to four times the daily need of it. While the portion of sardine provides 272 international units of vitamin D, and also, there are other types of fish rich in vitamin D, such as mackerel and halibut.
- Tuna: fresh or canned tuna contains 6.1 micrograms of vitamin D per 100 g.
- Shellfish: As shellfish live in saltwater, and is characterized by its low caloric content, and rich in nutrients, such as vitamin D. A 100 grams of wild oysters provides the body with more than half of its need for this vitamin, in addition to containing vitamin B12, copper, and zinc.In general, fish is an important source of vitamin D; in addition to all fish oils
1.3 Beef liver
Beef liver is among the foods that contain vitamin D in large amounts, essential amino acids, minerals, and other vitamins. It provides approximately 42 international units of vitamin D per about 85 grams of it. It is worth noting that one of the most important characteristics of this type of meat is tender compared to other types of meat.
1.4 Egg yolk
One egg yolk contains approximately (30 international units) of vitamin D.
1.5 Milk and its derivatives
Milk and some of its derivatives, such as milk and ricotta cheese, are the important foods that contain vitamin D and calcium. It is worth noting that cheese, in general, does not contain large amounts of vitamin D. However, ricotta cheese contains the highest amount of this vitamin compared to other types of cheese not supported. You should note that moderation is advised when consuming dairy products as part of the diet; since they are rich in fat as well, so as not to cause unnecessary weight gain.
2. Other sources of vitamin D
- Dark chocolate: is an interesting source of vitamin D. For this, it must contain more than 40% cocoa.
- Dietary supplements: Vitamin D is available in other sources that are different from nutrients, as it is in the form of a dietary supplement, which may be alone or may be added to other nutrient supplements such as calcium supplements. Although vitamin D supplements are generally safe, you must follow the instructions and keep it out of reach of children.
- Vitamin D and sun: Vitamin D is made in the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight or ultraviolet radiation, and the amount of vitamin D manufactured depends on several factors, including:
- Time of day: Where the sun's rays are stronger in the period between ten in the morning and three in the evening.
- Place of residence: The areas near the equator are exposed to high levels of ultraviolet radiation.
- The content of melanin in the skin: It is a dark pigment whose color ranges between brown and black. It gives the dark color to the skin, as it is found in the eyes and hair, and it is worth noting that the more skin content of this melanin pigment, the higher the need to be exposed to sunlight to obtain an adequate amount of vitamin D.
Related: What is the importance of a well-balanced and healthy diet?
3. Benefits of vitamin D for the body
Vitamin D is an important element to maintain the health of the body in several ways, and the benefits of obtaining adequate amounts of vitamin D include the following:
- Maintaining healthy bones
- The risk of influenza.
- Reducing the risk of diabetes, as a vitamin deficiency D adversely affects the secretion of insulin and glucose tolerance in people with type 2 diabetes.
- Cancer prevention: Vitamin D greatly influences the regulation of healthy cell growth, as it slows the development of cancer by slowing the growth and development of the blood vessels that feed cancerous tissues. Thus, increasing the chance of cancer cells dying, and reducing the chances of their proliferation and spread in the body in a process known as metastasis or cancer cell migration.
- Fighting many diseases: As vitamin D affects the immune system positively, vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, Alzheimer's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and severe asthma.
- Improve mood and prevent depression.
4. Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency
Include in general:
- Weakness and an inability to control joint mobility.
- Fatigue and severe pain in the bones.
- Having soft bone disease.
- Extreme and fast fatigue.
- Excessive sleepiness during the day.
- Anxiety and constant tension at night.
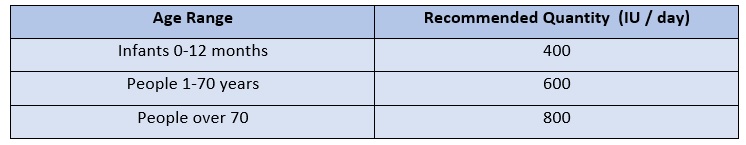
5. The body's need for vitamin D
The following table shows the recommended amount of vitamin D to meet the daily needs of the body, according to the age group: